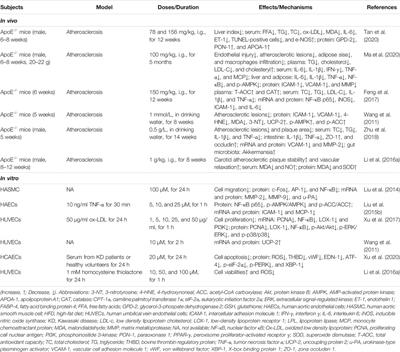
Traditional Chinese medicine plays a significant role in the treatment of various diseases and has attracted increasing attention for clinical applications. Vascular diseases affecting vasculature in the heart, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, and diabetic complications have compromise quality of life for affected individuals and increase the burden on health care services. Berberine, a naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloid form Rhizoma coptidis, is widely used in China as a folk medicine for its anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Promisingly, an increasing number of studies have identified several cellular and molecular targets for berberine, indicating its potential as an alternative therapeutic strategy for vascular diseases, as well as providing novel evidence that supports the therapeutic potential of berberine to combat vascular diseases. The purpose of this review is to comprehensively and systematically describe the evidence for berberine as a therapeutic agent in vascular diseases, including its pharmacological effects, molecular mechanisms, and pharmacokinetics. To this end, we screened articles on berberine treatment in vascular diseases published in the years 2010–2021 using Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) online databases and summarized the findings. According to data published so far, berberine shows remarkable anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-autophagic activity via the regulation of multiple signaling pathways, including AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), silent information regulator 1 (SIRT-1), hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF‐1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt), janus kinase 2 (JAK-2), Ca2+ channels, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Moreover, we discuss the existing limitations of berberine in the treatment of vascular diseases, and give corresponding measures. In addition, we propose some research perspectives and challenges, and provide a solid evidence base from which further studies can excavate novel effective drugs from Chinese medicine monomers.